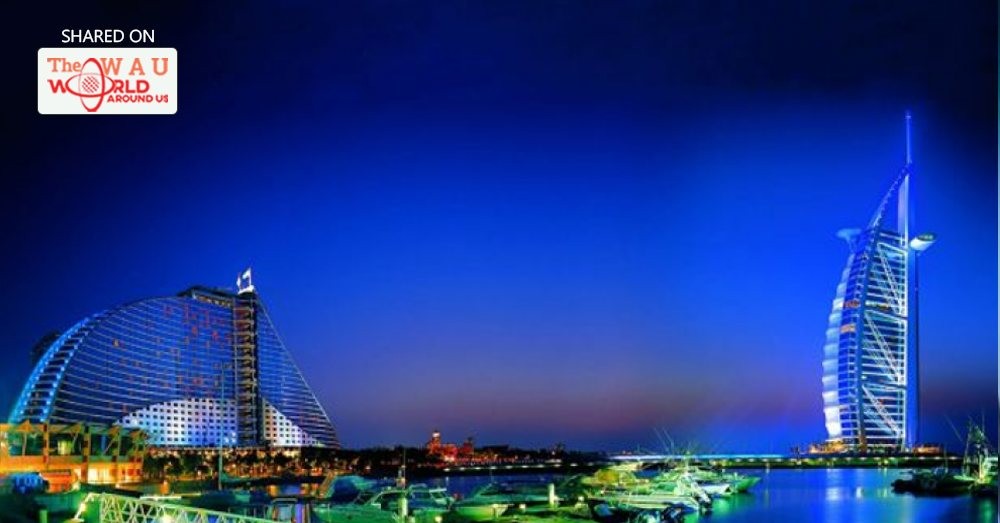
State of Dubai
Dubai is the most populous city in the UAE. It is located on the southeast coast of the Persian Gulf and is the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, one of the seven emirates that make up the country. Abu Dhabi and Dubai are the only two emirates to have veto power over critical matters of national importance in the country's legislature.The city of Dubai is located on the emirate's northern coastline and heads up the Dubai-Sharjah-Ajman metropolitan area. Dubai is to host World Expo 2020.
Dubai has emerged as a global city and business hub of the Middle East. It is also a major transport hub for passengers and cargo. By the 1960s, Dubai's economy was based on revenues from trade and, to a smaller extent, oil exploration concessions, but oil was not discovered until 1966. Oil revenue first started to flow in 1969. Dubai's oil revenue helped accelerate the early development of the city, but its reserves are limited and production levels are low: today, less than 5% of the emirate's revenue comes from oil. The emirate's Western-style model of business drives its economy with the main revenues now coming from tourism, aviation, real estate, and financial services.Dubai has recently attracted world attention through many innovative large construction projects and sports events. The city has become iconic for its skyscrapers and high-rise buildings, in particular the world's tallest building, the Burj Khalifa. Dubai has been criticised for human rights violations concerning the city's largely South Asian workforce.Dubai's property market experienced a major deterioration in 2008–09 following the financial crisis of 2007–08,but the emirate's economy has made a return to growth, with a projected 2015 budget surplus.
Dubai has been ruled by the Al Maktoum family since 1833; the emirate is an absolute monarchy with no elections (other than the few thousand Dubai citizens participating in the electoral college for the Federal National Council of the UAE). The ruler,Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, is also the Vice President and Prime Minister of the United Arab Emirates and member of the Supreme Council of the Union (SCU). Dubai appoints 8 members in two-term periods to the Federal National Council(FNC) of the UAE, the supreme federal legislative body.
The Dubai Municipality (DM) was established by the then-ruler of Dubai, Rashid bin Saeed Al Maktoum, in 1954 for purposes of city planning, citizen services and upkeep of local facilities.DM is chaired by Hamdan bin Rashid Al Maktoum, deputy ruler of Dubai, and comprises several departments such as the Roads Department, Planning and Survey Department, Environment and Public Health Department and Financial Affairs Department. In 2001, Dubai Municipality embarked on an e-Government project with the intention of providing 40 of its city services through its web portal, [ dubai.ae]. Thirteen such services were launched by October 2001, while several other services were expected to be operational in the future.Dubai Municipality is also in charge of the city's sanitation and sewage infrastructure.
The UAE has a Minister of Happiness, appointed by his High Highness Sheikh Mohammed Bin Rashid Al Maktoum. The UAE has also appointed a Minister of Tolerance to promote tolerance as a fundamental value of the UAE, a country filled with a diverse range of faiths and ethnicities,and also a Minister for Youth Affairs.
Economic and social development:
One of the world's fastest growing economies Dubai's gross domestic product is projected at US$107.1 billion, with a growth rate of 6.1% in 2014 Although a number of core elements of Dubai's trading infrastructure were built on the back of the oil industry revenues from oil and natural gas account for less than 5% of the emirate's revenues It is estimated that Dubai produces 50,000 to 70,000 barrels (7,900 to 11,100 m3) of oil a day and substantial quantities of gas from offshore fields. The emirate's share in the UAE's total gas revenues is about 2%. Dubai's oil reserves have diminished significantly and are expected to be exhausted in 20 years.Real estate and construction (22.6%),trade (16%), entrepôt (15%) and financial services (11%) are the largest contributors to Dubai's economy.
Dubai’s non-oil foreign trade stood at $362 billion in 2014. Of the overall trade volumes, imports had the biggest share with a value of $230 billion while exports and re-exports to the emirate stood at $31 billion and $101 billion respectively.
By 2014, China had emerged as Dubai's largest international trading partner, with a total of $47.7 billion in trade flows, up 29% from 2013. India was second among Dubai’s key trading partners with a trade of $29.7 billion, followed by the United States at $22.62 billion. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was Dubai’s fourth trading partner globally and first in the GCC and Arab world with a total trade value of $14.2 billion. Trade with Germany in 2014 totalled $12.3, Switzerland and Japan both at $11.72 billion and UK trade totalled $10.9 billion.
Historically, Dubai and its twin across Dubai Creek, Deira (independent of Dubai City at that time), were important ports of call for Western manufacturers. Most of the new city's banking and financial centres were headquartered in the port area. Dubai maintained its importance as a trade route through the 1970s and 1980s. Dubai has a free trade in gold and, until the 1990s, was the hub of a "brisk smuggling trade" of goldingots to India, where gold import was restricted. Dubai's Jebel Ali port, constructed in the 1970s, has the largest man-made harbour in the world and was ranked seventh globally for the volume of container traffic it supports. Dubai is also a hub for service industries such as information technology and finance, with industry-specific free zones throughout the city. Dubai Internet City, combined with Dubai Media City as part of TECOM (Dubai Technology, Electronic Commerce and Media Free Zone Authority), is one such enclave, whose members include IT firms such as Hewlett-Packard, EMC Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Microsoft, Delland IBM, and media organisations such as MBC, CNN, BBC, Reuters, Sky News and AP.
The government's decision to diversify from a trade-based, oil-reliant economy to one that is service- and tourism-oriented made property more valuable, resulting in the property appreciation from 2004 to 2006. A longer-term assessment of Dubai's property market, however, showed depreciation; some properties lost as much as 64% of their value from 2001 to November 2008. The large-scale real estate development projects have led to the construction of some of the tallest skyscrapers and largest projects in the world such as the Emirates Towers, the Burj Khalifa, the Palm Islands and the most expensive hotel, the Burj Al Arab. Dubai's property market experienced a major downturn in 2008 and 2009 as a result of the slowing economic climate. By early 2009, the situation had worsened with the Great Recession taking a heavy toll on property values, construction and employment. This has had a major impact on property investors in the region, some of whom were unable to release funds from investments made in property developments. As of February 2009, Dubai's foreign debt was estimated at approximately $80 billion, although this is a tiny fraction of the sovereign debt worldwide. Dubai real estate and UAE property experts believe that by avoiding the mistakes of the past, Dubai's realty market can achieve stability in the future.
The Dubai Financial Market (DFM) was established in March 2000 as a secondary market for trading securities and bonds, both local and foreign. As of fourth quarter 2006, its trading volume stood at about 400 billion shares, worth $95 billion in total. The DFM had a market capitalisation of about $87 billion. The other Dubai-based stock exchange is NASDAQ Dubai, which is the international stock exchange in the Middle East. It enables a range of companies, including UAE and regional small and medium-sized enterprises, to trade on an exchange with an international brand name, with access by both regional and international investors.
Dubai is also known as the City of Gold, because a major part of the economy is based on gold trades, with Dubai's total gold trading volumes in H1 2011 reaching 580 tonnes, with an average price of US$1,455 per troy ounce.
A City Mayors survey ranked Dubai 44th among the world's best financial cities in 2007, while another report by City Mayors indicated that Dubai was the world's 27th richest city in 2012, in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). Dubai is also an international financial centre and has been ranked 37th within the top 50 global financial cities as surveyed by the MasterCard Worldwide Centres of Commerce Index (2007), and 1st within the Middle East.
In 2012, the Global City Competitiveness Index by the Economist Intelligence Unit ranked Dubai at No. 40 with a total score of 55.9. According to its 2013 research report on the future competitiveness of cities, in 2025, Dubai will have moved up to 23rd place overall in the Index.Indians, followed by Britons and Pakistanis are the top foreign investors in Dubai realty.
Dubai has launched several major projects to support its economy and develop different sectors. These include Dubai Fashion 2020, and Dubai Design District, expected to become a home to leading local and international designers. The AED 4 billion first phase of the project will be complete by January 2015.
Location:
Dubai is a city found in Dubai, The United Arab Emirates. It is located 25.07 latitude and 55.17 longitude and it is situated at elevation 3 meters above sea level.
Topographic Features:
The United Arab Emirates consists mainly of sandy desert. It is bounded on the west by an immense sebkha, or salt flat, extending southward for nearly 112 km (70 mi). The eastern boundary runs northward over gravel plains and high dunes until it almost reaches the Hajar Mountains in the Ra's Musandam near Al 'Ayn. The flat coastal strip that makes up most of the United Arab Emirates has an extensive area of sebkha subject to flooding. Some sand spits and mud flats tend to enlarge, and others enclose lagoons. A sandy desert with limestone outcroppings lies behind the coastal plain in a triangle between the gravel plain and the mountains of the east and the sands of Sa'udi Arabia to the south. Far to the south, the oases of Al-Liwa' are aligned in an arc along the edge of dunes, which rise above 90 m (300 ft).
The main gravel plain extends inland and southward from the coast of Ra's al-Khaimah to Al 'Ayn and beyond. Behind Ra's al-Khaimah and separating Fujairah from the Persian Gulf is an area of mountains that rise over 900 m (3,000 ft) in height, with isolated cultivation. Finally, alluvial flats on the Gulf of Oman fill the bays between rocky spurs. South of Khor Fakkan (Sharjah), a continuous, well-watered fertile littoral strip known as the Batinah Coast runs between the mountains and the sea and continues into Oman. There are, in addition, many islands, most of which are owned by Abu Dhabi. These include Das, the site of oil operations, and Abu Musa, exploited for oil and red oxide.
Land Area:
The total land area of Dubai is approximately 4,114 km² square kilometers.
Population:
Top officials yesterday revealed that the number of people living in the emirate is expected to increase by about 1.2 million – a rise of more than 50 per cent – between now and 2020, when it will host the World Expo. The population of Dubai is currently 2.25 million.
Capital City:
Abu Dhabi
Official Language:
Dubai - Language. Although Arabic is the official language of the UAE, English is the most spoken language in Dubai. You will also find a lot of expatriates who speakHindi, Urdu, Bengali, Tamil, Tagalog, Persian, Chinese, Malayalam, in addition to many other languages.
Climate:
In the summer, the weather in Dubai is very hot, dry and humid, with temperatures reaching 45 °C (113 °F) for many days. Even the sea temperature reaches 37 °C (99 °F), with humidity averaging over 90%. The highest recorded temperature in Dubai is 52.1 °C (126 °F).
Major Towns:
Dubai,Abu Dhabi,Sharjah,Al Ain and others.
Currency:
United Arab Emirates Dirham
National Day:
2 December 2007
Public Holidays :
|
Sunday |
July 03 |
|
Wednesday |
July 06 |
|
Wednesday |
September 14 |
|
Sunday |
October 02 |
National flag:
The flag of the United Arab Emirates (Arabic: علم الإمارات العربية المتحدة) was adopted on December 2, 1971. It contains the Pan-Arab colors red, green, white, and black, which symbolize Arabian unity. Merchant ships may fly the alternative civil ensign, a red flag with the national flag in the canton.
Meaning of the flag:
National flag and ensign. Flag ratio: 1:2. The flag of the United Arab Emirates (Arabic: علم الإمارات العربية المتحدة) was adopted on December 2, 1971. It contains the Pan-Arab colors red, green, white, and black, which symbolize Arabian unity.
Work Hours:
Working Hours & Overtime. The working week in Dubai tends to vary between 40 and 48 hours, depending on the particular company's policy. Officehours are usually from 8.30 or 9.00 am to 5.30 or 6.00 pm, but some companies also split the working day into two, usually from 8.00 to 1.00 and 4.00 to 7.00.
Local Time:
UTC/GMT +4 hours
Electrical Current:
The electrical current in Dubai is 220/240 V, 50 Hz AC. British-style 3-pin electrical plugs are used (Type G or 13 amp plug).
Public Transport System:
The Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) was formed by the decree number 17 for the year 2005.
RTA is responsible for planning and providing the requirements of transport, roads & traffic in the Emirate of Dubai, and between Dubai and other Emirates of the UAE, neighboring countries in order to provide an effective & an integrated transport system.
Dubai Metro
The Dubai Metro currently operates two lines. The construction contract for the project was given to Dubai Rapid Link (DURL), a consortium led by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, in 2005. The construction of the red line began in September 2005 and the red line started operating on 9 September 2009, with its extension opened in 2010 and 2013. There are currently 29 stations on the red line. The construction of green line started in 2006 and the green line opened on 9 September 2011. There were initially 18 stations and two more stations were added in 2014. The Green Line runs from Etisalat to Creek and the Red Line from Rashidiya to Jebel Ali.
Bus
Dubai has a very large bus system run by the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) . The bus system has 193 routes on weekdays and transports over 30 million people weekly. The Public Transport bus system is large and advanced. Unfortunately, the number of buses does not increase with the same rate as the amount of passengers, which makes this problem worse as time progresses.
The (RTA) had announced that Dubai roads will see 1616 new buses. The buses will be of various sizes & models. The new fleet was expected to be fully operational by the end of 2008. Under brandname DubaiBus an extensive bus system is operated. Some buslines are feeders for the metro system. 656 of 1500 bus stops are equipped with airconditioned shelters. The bus fleet consists almost entirely of low floor European-made, air-conditioned buses by Neoplan, Mercedes-Benz, Solaris and VDL. Although the city of Dubai is growing year by year, the number of passengers is hardly rising. It is possible that this is a result of constant metro extensions.
Trams
As of April 2008, there were two expected tram systems to be built in Dubai by 2011. The first is the Downtown Burj Dubai Tram System, and the second is the Dubai Tram.
The Downtown Burj Dubai Tram System is a 4.6 km (2.9 mi) tram service that is planned to serve the area around the Burj Khalifa. Announced in April 2008 by Emaar, the Dh500 million system will have two separate lines. The first line, which is expected to open by the end of 2009, will run 1.1 kilometres (0.68 mi) from Dubai Metro's Burj Khalifa station to the Dubai Mall with one stop at The Address Dubai Mall. While this line will have trams running in both directions, the second line will only run in one direction. The second phase, expected to open in 2010, will serve ten stations. The 4.6 km loop will travel clockwise and will have a total travel time of eight minutes.
Ports and water travel
Abras at Bur Dubai
Dubai is served by two large commercial ports, Port Rashid and Port Jebel Ali. Various cruise ships dock in Dubai. Dubai Creek and Port Saeed are used by local traders in dhows.
One of the more traditional means of getting across Dubai Creek between Bur Dubai and Deira is on abras, small boats that ferry passengers across the Creek between stations in Bastakiya and Bani Yas Road, for a nominal charge of 1 UAE dirhams. They can be rented, along with an operator, for 100 UAE dirhams, approximately US$27.
The Marine Transport Agency, part of the Road and Transportation Agency, started the Dubai Water Bus System on Dubai Creek in July 2007. Years ago there used to be a seaplane service which used to take passengers to other parts of the emirates.
Air travel
Dubai International Airport is a hub for Emirates and FlyDubai and has a large duty-free shopping centre. The airport has won numerous awards for its excellence in design and services] A third terminal, which fully supports the new Airbus A380, was opened in October 2008 and doubled the airport's capacity. A new concourse catering to the A380 was completed in late 2012.
Al Maktoum International Airport, that opened on 27 June 2010., will make a new free trade area within Dubai and be the centerpiece of the Dubai World Central aerotropolis. The airport was announced in 2004 and construction began in January 2005. The first part was expected to be completed by 2008. Although initially intended as a predominantly cargo airport, plans are afoot for it to handle some 120 million passengers per annum within 20 years, which would likely surpass Atlanta'sHartsfield-Jackson International Airport as the world's busiest airport. Since 2013 only a handful of airlines operate out of Al Maktoum International Airport in terms of passenger services.
Sports:
Heritage and popular sports include camel and horse racing, falconry, endurance races, desert and marine sports, football, golf, tennis and even sand-skiing and ice-skating. Click here to view the sports clubs in Dubai. Dubai has firmly established itself as the sports capital in the Middle East.Jun 8, 2011
Telephone Code:
To call Dubai from abroad you need to dial the international country code for United Arab Emirates which is +971 and then you dial the area code followed by the local number. Local numbers are composed of seven digits. Landline area codes are two digit numbers.
Share This Post