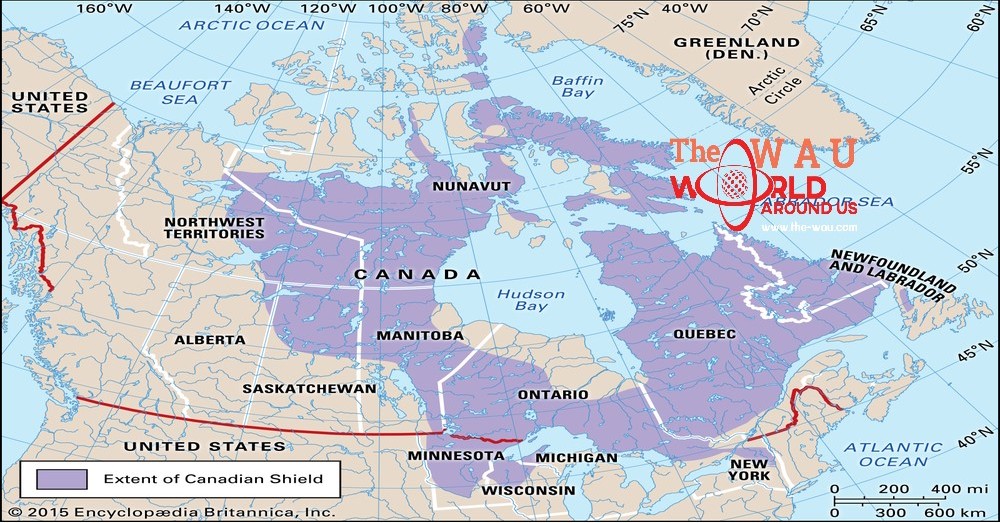
Canadian Shield, one of the world’s largest geologic continental shields, concentrated on Hudson Bay and lengthening for 8 million rectangular km (3 million rectangular miles) over eastern, central, and northwestern Canada from the Great Lakes to the Canadian Arctic and into Greenland, with small extensions into northern Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, and New York, U.S.
The Canadian Shield constitutes the largest mass of uncovered Precambrian rock at the face of Earth. The region, as a whole, consists of ancient crystalline rocks whose complicated shape attests to a long records of uplift and depression, mountain constructing (orogeny), and erosion. Some of the historical mountain stages can nonetheless be recognized as a ridge or belt of hills, however the gift appearance of the physical panorama of the Canadian Shield isn't always so much a end result of the folding and faulting and compression of the rocks hundreds of thousands of years ago as it's miles the work of ice in relatively latest geologic time. During the Pleistocene Epoch (2.6 million to 11,seven-hundred years in the past), the great continental glaciers that blanketed northern North America had this vicinity as a centre. The ice, in moving to the south, scraped the land naked of its overlying mantle of weathered rock. Some of this cloth changed into deposited at the shield when the ice melted, however the bulk of it became carried southward to be deposited south and southwest of the Canadian Shield.
The resulting surface consists of rocky, ice-smoothed hills with an average alleviation of 30 metres (100 feet), together with abnormal basins, which are often filled via lakes or swamps. In places the vintage mountain degrees may be diagnosed by way of hills several loads of metres in height. The northeastern portion, however, have become tilted up so that, in northern Labrador and Baffin Island, the land rises to greater than 1,500 metres (5,000 feet) above sea level.
By far the most important of Canada’s physiographic regions, the Canadian Shield (on occasion known as the Precambrian Shield) occupies about half of the total vicinity of the us of a and is concentrated on Hudson Bay. The protect consists of some of the world’s oldest rocks, which had been folded by using mountain-constructing actions and cut down with the aid of erosion till the region changed into reduced almost to a plain. It turned into warped and folded in places, so elements of it now stand much higher than others, specially around its outer edges. In the north the rim is ready 7,000 feet (2,000 metres) above sea level, and fjords with partitions from 2,000 to 3,000 feet (six hundred to 900 metres) excessive extend many miles into the mountain masses. The Labrador Highlands, including the Torngat, Kaumajet, and Kiglapait mountains, lie south of Hudson Strait. Along the north shore of the St. Lawrence River in Quebec, the defend rim is a 2,000-foot (600-metre) escarpment, the Laurentide Scarp. The rim is sort of imperceptible in southern Ontario, however in northern Ontario it rises again to nearly 1,500 feet (450 metres) above the northern shore of Lake Superior. From Manitoba northwestward, the guard part is marked by using a huge variety of lakes.
Most of the guard lies at elevations beneath 2,000 feet (six hundred metres). Its loss of hills of any size produces a typically monotonous landscape, however geologically recent glaciations have had a striking impact at the floor. the ridges occupied by way of sizeable numbers of lakes. In other regions the glaciers deposited till or moraine at the surface and in still others left massive fields of erratics (boulders and other material extraordinary from local bedrock). Eskers—long, slim ridges of deposits—stretch across the shield, now and again for extra than a hundred miles (160 km), marking the path of antique, subglacial rivers. In still other locations, deposits laid down through glacial lakes that have seeing that drained away have given upward push to sizable clay belts. The guard includes a massive form of minerals (e.G., copper, silver, and gold), and its exploitation has been a essential source of Canada’s wealth.
Share This Post