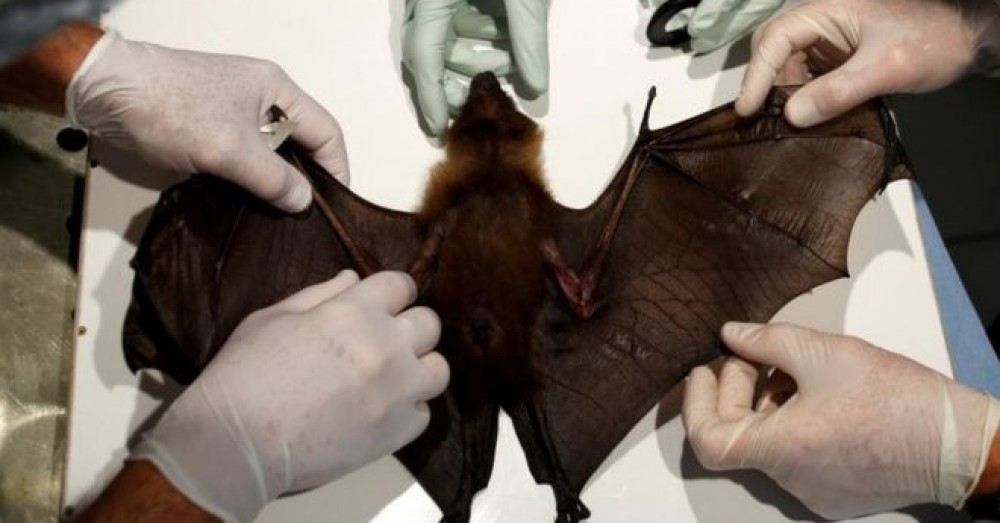
Zoonotic diseases - which jump from animals to humans - are increasing and will continue to do so without action to protect wildlife and preserve the environment, UN experts have warned.
They blame the rise in diseases such as Covid-19 on high demand for animal protein, unsustainable agricultural practices and climate change.
Neglected zoonotic diseases kill two million people a year, they say.
Covid-19 is set to cost the global economy $9tn (£7.2tn) over two years.
Why are we catching more diseases from animals?
Ebola, West Nile virus and Sars are also all zoonotic diseases: they started in animals, and made the jump to humans.
What did the report say?
But that jump is not automatic. It is driven, according to the report by the United Nations Environment Programme and the International Livestock Research Institute, by the degradation of our natural environment - for example through land degradation, wildlife exploitation, resource extraction and climate change. This alters the way animals and humans interact.
"In the last century we have seen at least six major outbreaks of novel coronaviruses," said Inger Andersen, under-secretary general and executive director of the UN Environment Programme.
"Over the last two decades and before Covid-19, zoonotic diseases caused economic damage of $100bn (£80bn)."
She said that "two million people in low- and middle-income countries die each year from neglected endemic zoonotic diseases - such as anthrax, bovine tuberculosis and rabies".
"These are often communities with complex development problems, high dependence on livestock and proximity to wildlife."
Meat production, for example, has increased by 260% in the last 50 years, Ms Andersen said.
"We have intensified agriculture, expanded infrastructure and extracted resources at the expense of our wild spaces," she explained.
"Dams, irrigation and factory farms are linked to 25% of infectious diseases in humans. Travel, transport and food supply chains have erased borders and distances. Climate change has contributed to the spread of pathogens."
Share This Post