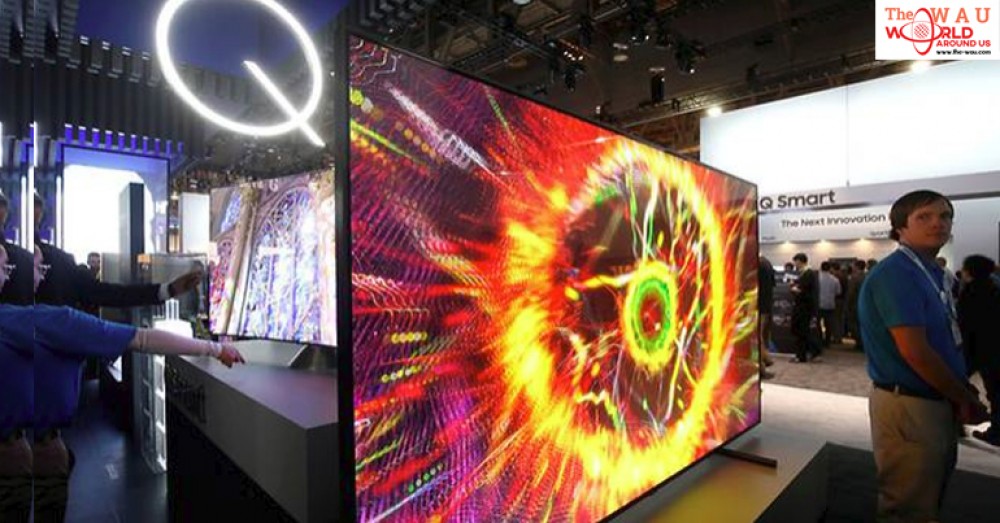
At the 2013 annual Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas, flashy organic light-emitting diode (OLED) televisions sporting credit card-thin screens were at the front and centre of Samsung Electronics' new gadgets display.
Later that year, the South Korean company splurged on marketing the televisions – which then retailed at around US$10,000 for the 55-inch model – to the ultra wealthy. Among the promotions was a penthouse party for the residents of One Hyde Park in London, labelled the world's most expensive residential block.
But by 2015, it had stopped making OLED TVs, saying the market was not ready to embrace the high costs of the technology – based on thin films of carbon-based modules that light up in response to electric current.
Instead it decided to focus on developing liquid crystal display screens that are backlit and enhanced with so-called quantum dots, semiconductor nanocrystals that produce colours and can improve picture quality. These are known as QLED TVs.
It appears to have been a costly misstep. OLED TVs have become a dominant technology in the premium market – that is for a TV of at least 55 inches in size costing more than US$2,500 - as the cost of producing them has dropped dramatically.
Samsung is now the only major TV manufacturer not to produce OLED screens. And while the TV business generates less than 3 per cent of Samsung’s profit, which largely comes from its semiconductor and mobile phones businesses, the loss of the leadership of the premium, higher-margin market is a hard blow.

Samsung declined to comment on whether ending OLED TV production was a costly mistake or who made it.
A look at online reviews of both OLED and QLED TVs in the past couple of years indicate that OLED TVs made by South Korea’s LG Electronics and Japan’s Sony gained fans because of the quality of the picture. In particular, reviewers cited more realistic colours and high resolution, as well as attractive designs and increasingly reasonable prices.
That doesn’t mean the Samsung QLED TVs don’t have their supporters. Picture quality has also improved and prices have dropped but they don’t tend to be reviewers’ top picks.
"OLED TV's jump in premium TV market share is a direct result of its outstanding picture quality," said Ross Young, CEO of research provider Display Supply Chain Consultants. "Samsung may have missteped in their 2017 product by emphasizing design over picture performance."
Samsung last year only got an 18.5 per cent share of global sales for premium TVs, based on dollar revenue, down from 54.7 per cent in 2015, according to research firm IHS Markit. Meanwhile, Sony and LG have leapfrogged Samsung to grab 36.9 per cent and 33 per cent of the market respectively. To be sure, Samsung remains the biggest maker of TVs in the world – a title it has now held for 12 years. It also claims to be No.1 in premium TVs, with more than a 40 per cent market share, based on data from GfK. These figures include 55-inch TVs that are cheaper than the US$2,500 IHS uses to define the segment.
MORE EFFICIENT MANUFACTURING
Samsung Electronics’ decision to base its TV business on LCD technology was made after it took the advice of Samsung Group's now-defunct Corporate Strategy Office, a source with knowledge of the matter said. "The office made a suggestion that it would be more profitable to focus on LCDs than switching to less-proven OLED," said the source, who declined to be named due to the sensitivity of the matter.
The reasons: the TV business was battling falling profits and the company felt LCD technology could be more profitable than high cost OLED, the source said. The only problem was that around the time this decision was being taken, LG was developing a much more efficient manufacturing process to make OLED screens.
The retail price of a mainstream LG 55-inch OLED TV has dropped to just 3 million won (US$2,811) this year from 15 million won (US$14,056) in 2013, LG said.
It is not the first time decisions involving Samsung’s Corporate Strategy Office have been questioned. The office, which was led by then Samsung Electronics vice chairman Choi Gee-sung, was closed after it faced criticism during the political scandal that led to the arrest of the group's heir Jay Y.
Lee last year on charges of bribery and embezzlement. Lee, who denies any wrongdoing, walked out a free man in February after an appeals court suspended his sentence.
Samsung told Reuters the biggest reason it is not making OLED TVs is the issue of screen burn-in, referring to a form of image retention when an image has been on the screen for a long time. LG, though, says on its U.S. website that while burn-in is possible on almost any display, it has addressed the issue through technology that protects against damage to the screen and rectifies short-term problems.
...[ Continue to next page ]
Share This Post